Active Directory (AD) Group Policy Objects (GPOs) are used to centrally manage user account settings, system configurations, and access to network resources. Here are some of the important benefits of using GPOs to configure shortcuts on user desktops:
Decide where the shortcut should appear on the user systems, and specify the exact location path.
Open the Run dialog box >> Type gpedit.msc >>Click OK

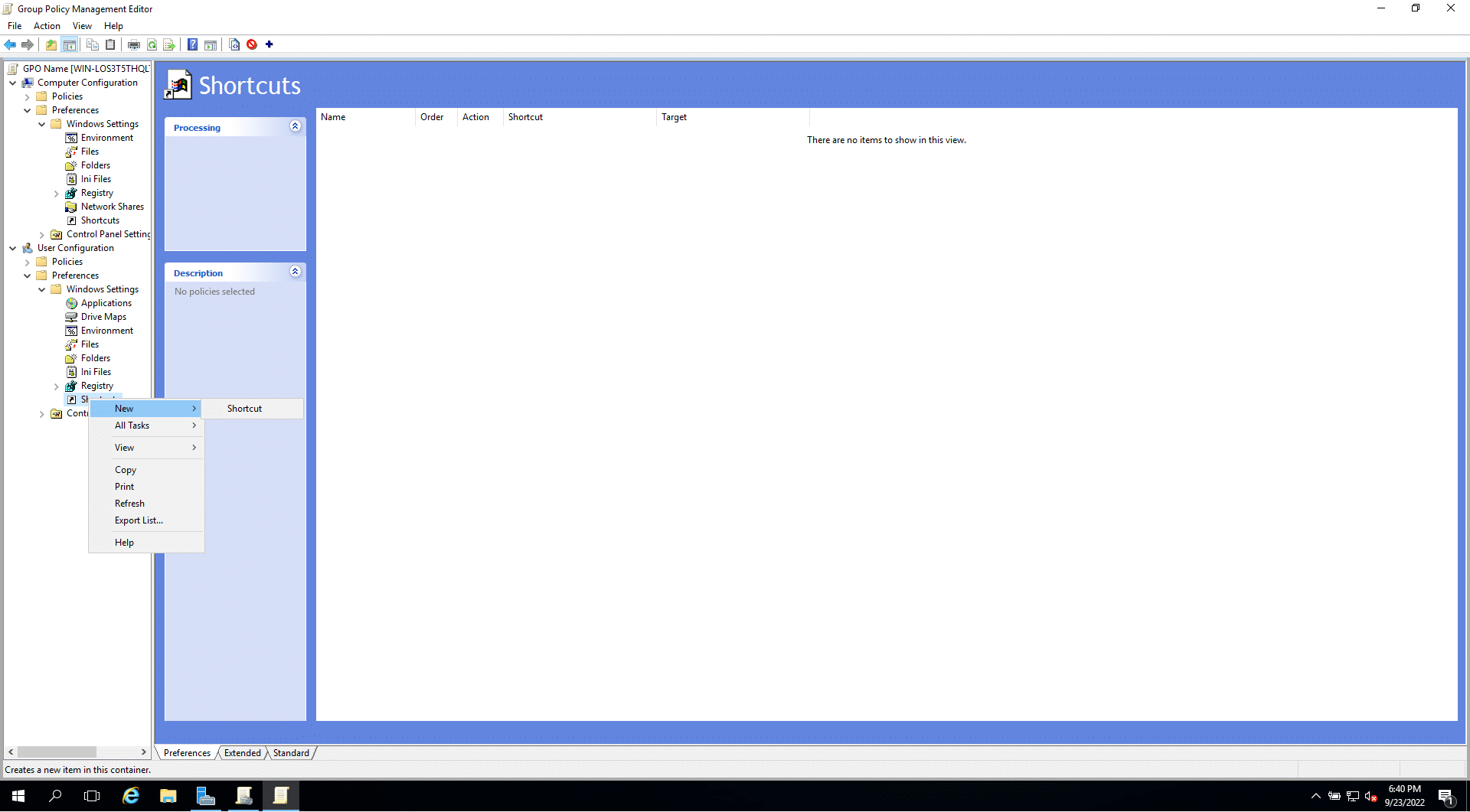
The shortcut settings window will open. The following are some of the important fields to be customized:
Actions: Create, Update, Replace, or Delete [View in detail]
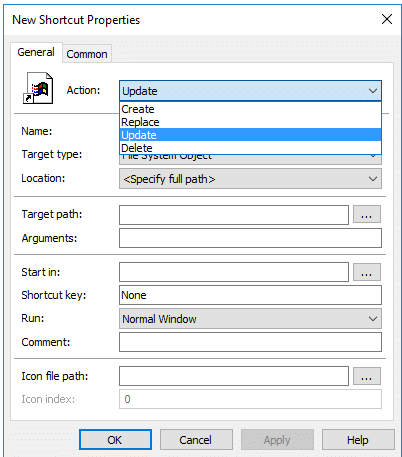
Target type: File System Object, URL, or Shell Object
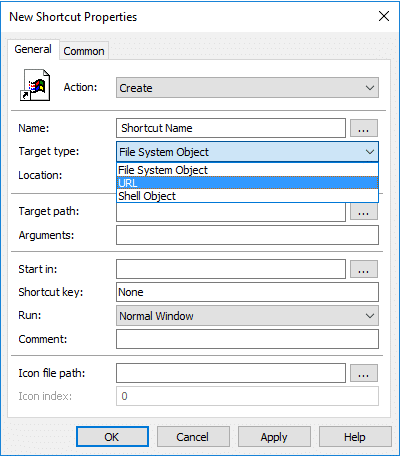
Location: Enter where the shortcut should appear in the targeted systems. /
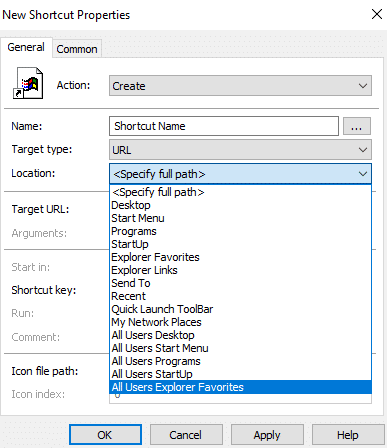
Target Path, URL, or Object: Enter where the shortcut will lead to when clicked.
Shortcut Key: Enter the combination of keys to open the shortcut.
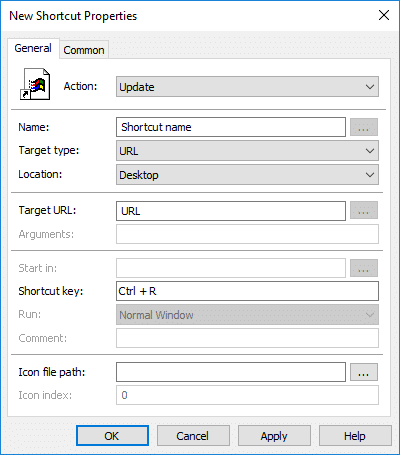
Icon file path: If you have an icon image associated with the shortcut, you can enter the path of the icon file here.
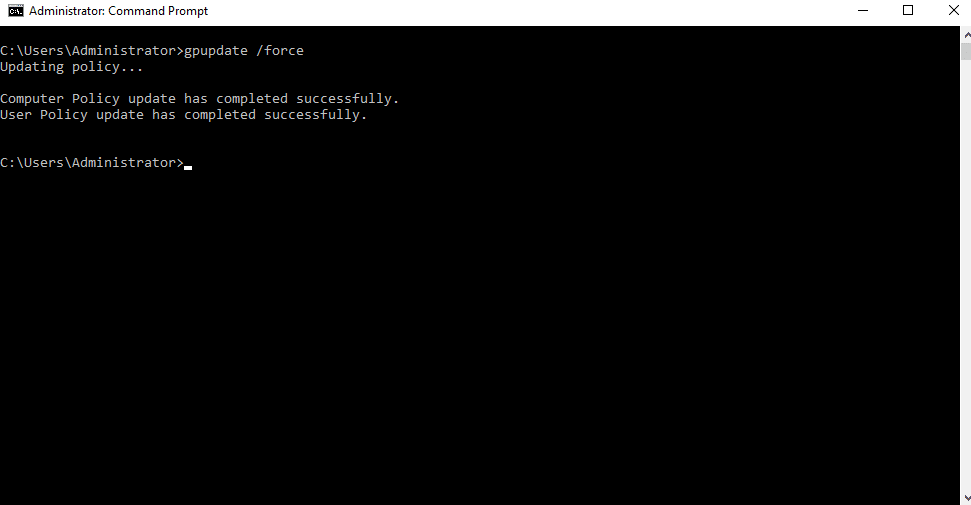
Once you have edited all the settings, open your Windows Command Prompt, run the gpupdate /force command, and reboot your system to implement the new Group Policy changes immediately.
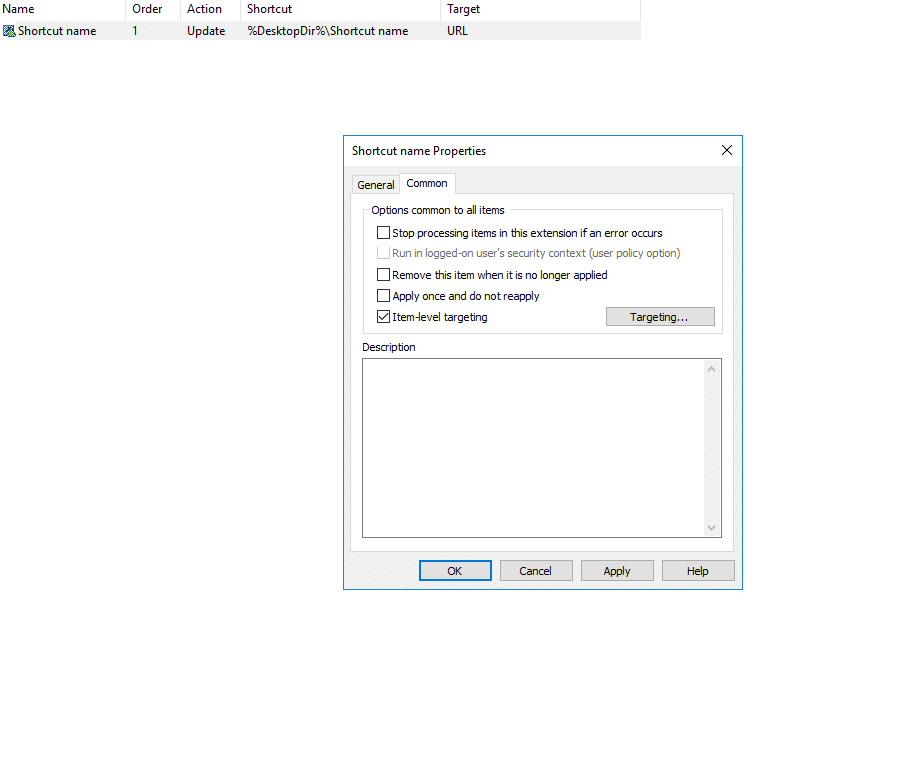
In the shortcut properties dialog box, you can see two tabs: General and Common. The General tab is used to add and modify shortcuts as mentioned in Step 3. The Common tab is used to configure user-level targeting.
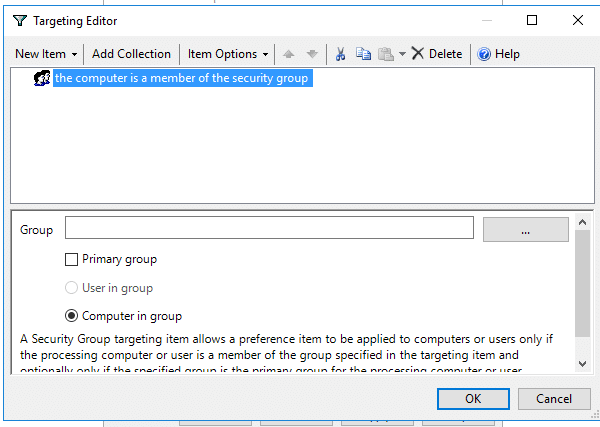
Go to the shortcut properties > click the Common tab > check the Item-level targeting option > click Targeting… > New Item.
A list of options will be displayed to target specific systems based on IP address range, network connection, operating system, CPU speed, RAM, site, terminal session etc.
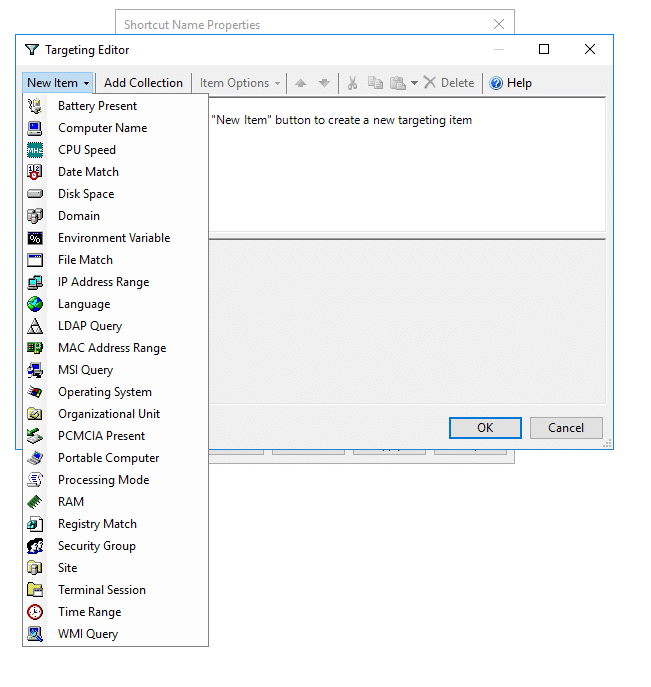
You can also define a security group and add that to the item-level targeting.
Deleting the shortcuts on user systems or deleting the GPO on the domain controller using the GPMC will be ineffective. You need to change the GPO Actions to Delete and apply the settings to remove the shortcuts permanently from the user systems.